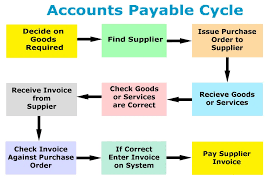
What is Accounts Payable Ledger?
An Accounts Payable Ledger is a record-keeping system used by businesses to track and manage their unpaid bills and invoices. It is like a big book or computer file that keeps track of all the money a company owes to its suppliers, vendors, and other creditors.
Think of it as a personal to-do list for a business. When a company receives an invoice for goods or services it has received but hasn’t paid for yet, that invoice is recorded in the accounts payable ledger. The ledger includes important information like the name of the supplier, the amount owed, the due date for payment, and any other relevant details.
The accounts payable ledger helps the business stay organized and keep track of its financial obligations. It allows the company to see at a glance how much money it owes to different suppliers and when those payments are due. By maintaining an accurate accounts payable ledger, businesses can avoid late payment penalties and maintain good relationships with their suppliers.
In summary, an accounts payable ledger is a tool used by businesses to keep track of the money they owe to others. It helps them stay organized and ensure they pay their bills on time.
Table of Contents
Importance of Accounts Payable Ledger in a Business
The Accounts Payable Ledger is important for businesses for a few reasons:
- Organization: The ledger helps businesses stay organized by keeping track of all the money they owe to suppliers and vendors. It provides a central place to record and manage all the unpaid bills and invoices.
- Timely Payments: The ledger helps businesses keep track of when payments are due. By having this information readily available, they can make sure they pay their bills on time and avoid any late payment fees or penalties.
- Cash Flow Management: Managing cash flow is crucial for businesses. The accounts payable ledger allows them to see how much money they need to pay out in the near future. By having this information, they can better plan and manage their available funds to ensure they can cover their expenses.
- Maintaining Relationships: Suppliers and vendors are important partners for a business. The accounts payable ledger helps businesses maintain good relationships by ensuring timely payments. Paying suppliers on time can help build trust and strengthen the business’s reputation.
- Financial Accuracy: The accounts payable ledger provides a detailed record of all the financial obligations of a business. This information is crucial for accurate financial reporting and helps ensure that the business’s financial statements reflect the true state of its liabilities.
In summary, the accounts payable ledger is important for businesses because it helps them stay organized, make timely payments, manage cash flow, maintain relationships with suppliers, and ensure accurate financial reporting.
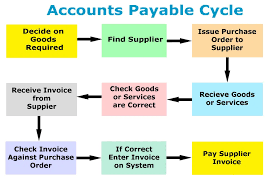
Main Characteristics of Accounts Payable Ledger in a Business
The main characteristics of an Accounts Payable Ledger in a business are:
- Record-Keeping: The accounts payable ledger is like a big record book or computer file that keeps track of all the unpaid bills and invoices a business has. It serves as a central place to store and organize this information.
- Supplier Information: The ledger includes important details about the suppliers and vendors the business owes money to. It records their names, contact information, and any other relevant details that help identify them.
- Invoice Details: For each unpaid bill or invoice, the ledger includes specific information such as the amount owed, the due date for payment, and a description of the goods or services provided.
- Tracking Payments: The ledger allows the business to keep track of payments made towards each bill or invoice. It helps monitor which payments have been made, when they were made, and the remaining amount still owed.
- Due Dates: The ledger highlights the due dates for payments, making it easy for the business to see which bills are coming up for payment and avoid missing any deadlines.
- Financial Control: The accounts payable ledger helps the business maintain financial control by providing a clear overview of its outstanding liabilities. It allows them to assess the total amount they owe to suppliers and manage their cash flow accordingly.
- Reporting: The ledger provides valuable information for financial reporting purposes. It helps create accurate reports on the business’s liabilities and outstanding obligations, ensuring that the financial statements are reliable and reflect the true financial position.
In simple terms, the accounts payable ledger is a record-keeping system that stores information about unpaid bills and invoices. It helps businesses keep track of what they owe, when payments are due, and ensures accurate financial reporting.
Uses of Accounts Payable Ledger in an Accounting
The Accounts Payable Ledger serves several important uses in accounting:
- Payment Tracking: The ledger helps track and monitor payments made to suppliers and vendors. It allows accountants to record when payments are made, the method of payment, and the date of payment. This information helps ensure accurate financial records and reconciliation of accounts.
- Expense Management: The ledger aids in managing and controlling expenses related to accounts payable. By recording and organizing invoices and bills in the ledger, accountants can easily track and analyze the business’s spending patterns, identify cost-saving opportunities, and make informed decisions regarding cash flow management.
- Cash Flow Planning: The accounts payable ledger is instrumental in managing cash flow effectively. By keeping track of the amounts due and their respective due dates, accountants can project future cash outflows, enabling the business to plan its cash reserves accordingly and avoid liquidity issues.
- Vendor and Supplier Relations: The ledger plays a vital role in maintaining positive relationships with vendors and suppliers. It ensures that payments are made in a timely manner, helping to establish trust and reliability. Having an accurate accounts payable ledger also allows for easy reference in case of any payment disputes or discrepancies.
- Financial Reporting: The accounts payable ledger provides essential data for financial reporting purposes. It helps accountants compile accurate financial statements, such as balance sheets and income statements, by including the liabilities and expenses related to accounts payable. This information is crucial for assessing the business’s financial health and making informed decisions.
- Auditing and Compliance: The accounts payable ledger serves as a valuable resource during audits and ensures compliance with accounting regulations. It provides a comprehensive record of transactions and payments, allowing auditors to verify the accuracy of financial statements and assess internal controls.
In summary, the accounts payable ledger is used in accounting to track payments, manage expenses, plan cash flow, maintain vendor relationships, facilitate financial reporting, and support auditing and compliance processes. It is a fundamental tool for maintaining accurate and reliable financial records within a business.
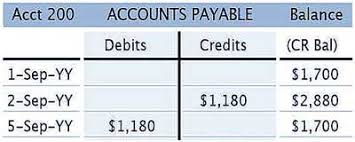
An Example of Accounts Payable Ledger in a Big Size Company
Let’s take the example of a fictional company called XYZ Corporation, which is a large manufacturing company. XYZ Corporation regularly purchases raw materials, equipment, and services from various suppliers and vendors. The Accounts Payable Ledger for XYZ Corporation would serve as a record-keeping system for all its unpaid bills and invoices.
In the ledger, XYZ Corporation would have separate accounts for each supplier or vendor they owe money to. For instance, let’s say XYZ Corporation has an account with Supplier A and another with Supplier B.
Under each supplier account, the ledger would include the following information:
- Supplier Information: The name, contact details, and any other relevant information about Supplier A and Supplier B.
- Invoice Details: For each bill or invoice received from Supplier A or Supplier B, the ledger would record important details such as the invoice number, invoice date, the goods or services provided, and the amount owed.
- Due Dates: The ledger would highlight the due dates for each invoice, indicating when the payment is expected to be made. For example, if Supplier A provides XYZ Corporation with a 30-day payment term, the due date would be recorded accordingly.
- Payment Tracking: As payments are made to Supplier A or Supplier B, the ledger would be updated to reflect the amount paid, the payment date, and the method of payment (e.g., check, electronic transfer).
- Reconciliation: Regularly, the accounts payable ledger would be reconciled with bank statements and other financial records to ensure that all payments made are accurately reflected and to identify any discrepancies or outstanding invoices.
This accounts payable ledger would be maintained and updated by the accounting department of XYZ Corporation. It would help the company stay organized, keep track of its financial obligations, ensure timely payments to suppliers, and provide accurate information for financial reporting.
By maintaining an accurate accounts payable ledger, XYZ Corporation can monitor its outstanding liabilities, manage cash flow effectively, maintain good relationships with suppliers, and comply with accounting regulations. It serves as a crucial tool for financial management and helps XYZ Corporation maintain control over its accounts payable processes.
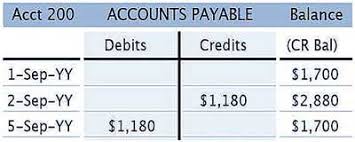
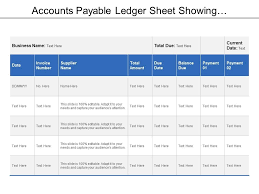
Process to Pass Entries in Accounts Payable Ledger
To pass entries in the Accounts Payable Ledger, you would typically follow these steps:
- Receive the Invoice: When your company receives an invoice from a supplier for goods or services, it serves as a record of the amount owed. The invoice includes details such as the supplier’s name, invoice number, date, and the amount due.
- Verify the Invoice: Review the invoice to ensure its accuracy. Check if the goods or services were received as stated and if the prices and quantities match the agreed-upon terms.
- Record the Invoice: Create an entry in the Accounts Payable Ledger for the invoice. Include the supplier’s name, invoice number, invoice date, and the amount owed. This entry establishes a liability for your company, as it owes the supplier the specified amount.
- Assign a Due Date: Determine the payment due date based on the agreed-upon terms with the supplier. This due date represents the deadline by which your company should make the payment.
- Monitor Payments: As payments are made to suppliers, update the Accounts Payable Ledger to reflect the amounts paid and the payment dates. Subtract the payment amount from the outstanding balance in the ledger.
- Reconcile the Ledger: Regularly reconcile the Accounts Payable Ledger with bank statements and other payment records to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies. This step ensures that all payments made are properly recorded and any outstanding invoices are addressed.
It’s important to note that the specific process may vary depending on the accounting system used by your company. Some companies may use software or accounting systems that automate these steps and facilitate the management of the Accounts Payable Ledger.
By following these steps and maintaining an accurate Accounts Payable Ledger, you can effectively track and manage your company’s outstanding liabilities, ensure timely payments to suppliers, and maintain financial control.